Step1.
Risk Identification
- Evaluate major climate events with a risk matrix to identify the frequency and impact of risk events
- Identify the financial implications of prioritized physical and transition risks
Step2.
Risk Control / Mitigation
- Incorporating climate risk as a key issue in continuous management
- Develop response strategies and monitoring mechanisms for climate risks
Step3.
Risk Monitoring / Reporting
- Continuous monitoring and management of climate risks through the Business Continuity Management (BCM) committee, combined with operational practices to demonstrate organizational resilience
Climate Risk and Opportunity Identification
ASUS identifies priority physical and transition risks based on the impact magnitude and frequency/probability of risk occurrences. These include:
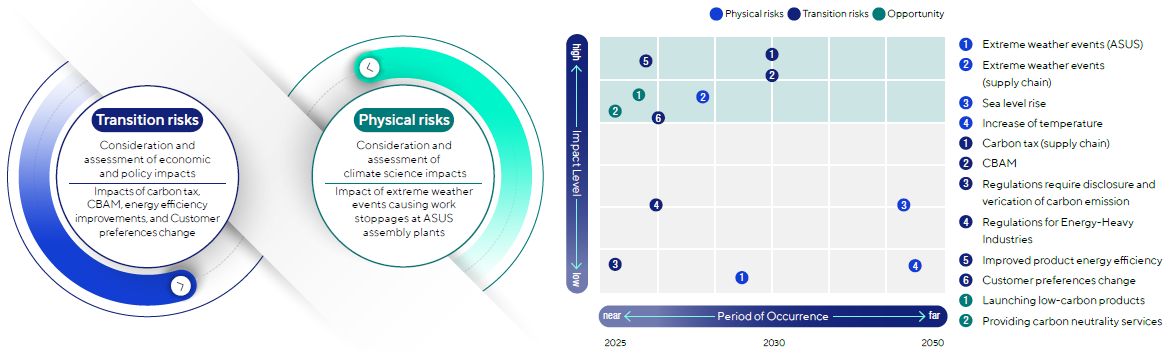
Transition Risks
In order to respond to the complexity and impact of the market caused by climate change, we must adjust the supply and demand with various methods, including policy, law, technology, and market changes to mitigate and adapt to the needs of climate change prevention.
- Carbon pricing - Increase in operating cost / expense caused by carbon tax in Mainland China
- Carbon pricing - Increase in operating cost / expense caused by CBAM
- Changes in Customer Behavior
Physical Risks
The actual risks caused by long-term climate change and immediate extreme weather disasters would have a direct impact on the industry and supply chain disruptions.
- Extreme Weather Events - Assembly Plant Shutdown due to Power Outage
- Extreme Weather Events - Land Transportation Disruption
Climate Change Opportunities
According to the IPCC AR6, the process of supporting sustainable development through mitigation and adaptation actions is referred to as “Climate Resilient Development.” To address actual or anticipated climate impacts, ASUS evaluates potential opportunities under climate change by managing greenhouse gas reductions and adaptation measures. For ASUS, climate mitigation opportunities primarily stem from reducing the carbon footprint of its products and offering low-carbon products to customers. Climate adaptation opportunities derive from the ASUS Carbon Partner Services, which not only assist customers in achieving net-zero targets but also, by procuring high-quality nature-based carbon credits, indirectly protect forests and slow the pace of climate change.
Risk Reduction Opportunities
Reducing the sources of greenhouse gases (GHGs) through human efforts
- Increase Revenue from Green Products
Risk Adaptation Opportunities
Propose ways to avoid climate impacts and create opportunities to improve climate change when adapting to actual or expected weather condition and its impacts
- Providing Carbon Partner Services

